In this article we will explore how to configure Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) on Enterprise SONiC. We will cover:
- BGP overview
- Configuring BGP with local ASN
- Establishing BGP neighbor relationships
- Advertising networks
- Verifying BGP sessions and routes
BGP Overview
BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) is a path-vector routing protocol widely used to exchange routing information between Autonomous Systems (ASes) and within large-scale networks. In Enterprise SONiC, BGP serves several critical roles:
- Data center fabric routing — distributing Layer 3 routes across leaf-spine topologies.
- EVPN-VXLAN control plane — signaling MAC/IP reachability for overlay networks.
- WAN edge peering — connecting enterprise networks to service providers or external ASes.
Key concepts:
- ASN (Autonomous System Number) — uniquely identifies an AS.
- Neighbors (Peers) — routers that establish a TCP session to exchange BGP routes.
- Network statement — advertises IP prefixes into BGP (used to originate routes).
Enabling BGP
By default, BGP is disabled on Enterprise SONiC. To enable it, you need to:
- Assign a local Autonomous System Number (ASN).
- Configure at least one BGP neighbor (peer).
BGP in SONiC does not automatically discover peers — all neighbors must be configured manually. Once a TCP session is established between peers:
- They exchange full routing information (full routing table on initial session).
- The session is maintained using keepalive messages to ensure connectivity.
Configuring BGP with Local ASN
Use the following command to enter BGP configuration mode and assign a local AS:
sonic(config)# router bgp [vrf <vrf-name> ]
• <Local_asn>: Local AS number (1–4294967295)
• <vrf-name>: Optional — specify a VRF for tenant isolation
Example
sonic(config)# router bgp 100Configuring BGP Router ID
The Router ID uniquely identifies the BGP instance. If not set manually, SONiC automatically selects the highest IPv4 address on the device (excluding management).
You can configure the Router-ID manually as per the example below:
Example
sonic(config)# router bgp 100
sonic(config-router-bgp) # router-id 1.1.1.1
Note that changing the router-ID resets all active BGP sessions.
Configure BGP Neighbors
To define a BGP neighbor (peer), use the neighbor command with either an IP address or an interface.
sonic(config)# router bgp 100
sonic(config-router-bgp) # neighbor <ip-address>
Then, specify the neighbor’s AS number.
sonic(config)# router bgp 100
sonic(config-router-bgp) # neighbor <ip-address>
sonic(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# remote-as <asn | internal | external>
sonic(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# description <text>
Activate the Address Family
Once the neighbor is defined, activate the IPv4 unicast address family to start exchanging routes.
SONiC supports IPv4, IPv6 and l2vpn address families.
sonic(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# address-family ipv4 unicast
sonic(conf-router-bgp-neighbor-af)# activate
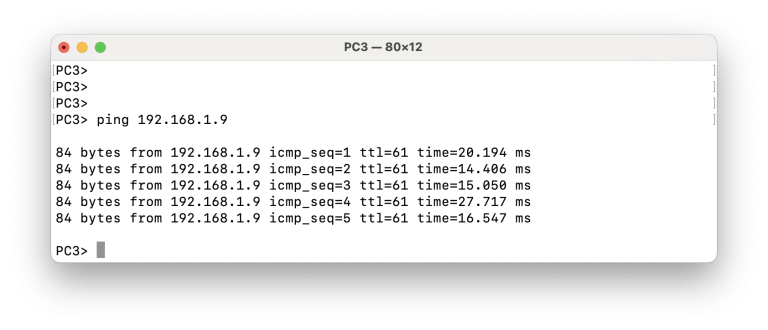
Topology
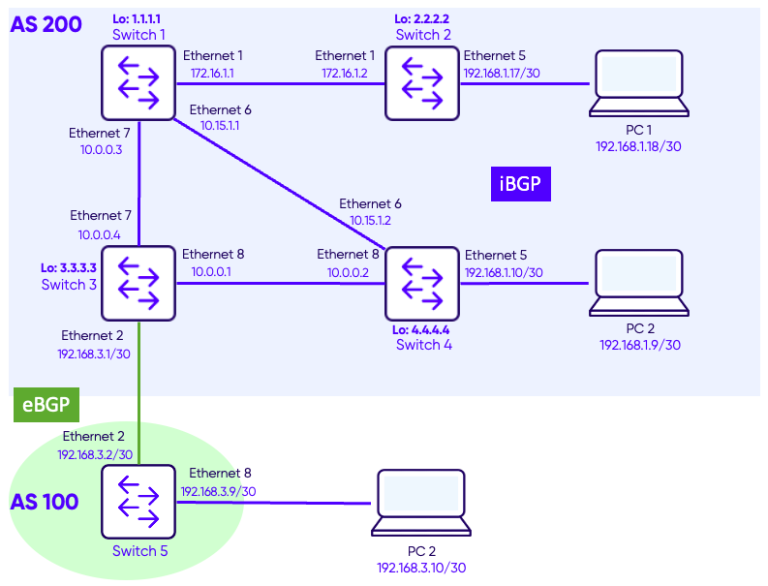
Configuration
Step 1 – Configuring iBGP in AS 200
Switches Switch-1, Switch-2, Switch-3 and Switch-4 are in the same Autonomous System and are configured as follows.
We assume that the interface are configured with the correct IP addresses and they are enabled. We also assume that OSPF is configured in ASN 200 and that the loopback IP addresses of the 4 switches are advertised throughout the network using OSPF.
For OSPF configuration, refer to the SONiC OSPF Configuration blog.
Switch-1
Switch-1(config)# router bgp 200
Switch-1(conf-router-bgp)# router-id 1.1.1.1
Switch-1(conf-router-bgp)# neighbor 2.2.2.2
Switch-1(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# remote-as 200
Switch-1(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# update-source interface Loopback 0
Switch-1(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# address-family ipv4 unicast
Switch-1(conf-router-bgp-neighbor-af)# activate
Switch-1(config-router-bgp-neighbor-af)# exit
Switch-1(config-router-bgp-neighbor)# exit
Switch-1(conf-router-bgp)# neighbor 3.3.3.3
Switch-1(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# remote-as 200
Switch-1(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# update-source interface Loopback 0
Switch-1(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# address-family ipv4 unicast
Switch-1(conf-router-bgp-neighbor-af)# activate
Switch-1(config-router-bgp-neighbor-af)# exit
Switch-1(config-router-bgp-neighbor)# exit
Switch-1(conf-router-bgp)# neighbor 4.4.4.4
Switch-1(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# remote-as 200
Switch-1(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# update-source interface Loopback 0
Switch-1(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# address-family ipv4 unicast
Switch-1(conf-router-bgp-neighbor-af)# activate
Switch-2
Switch-2(config)# router bgp 200
Switch-2(conf-router-bgp)# router-id 2.2.2.2
Switch-2(conf-router-bgp)# neighbor 1.1.1.1
Switch-2(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# remote-as 200
Switch-2(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# update-source interface Loopback 0
Switch-2(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# address-family ipv4 unicast
Switch-2(conf-router-bgp-neighbor-af)# activate
Switch-2(config-router-bgp-neighbor-af)# exit
Switch-2(config-router-bgp-neighbor)# exit
Switch-2(conf-router-bgp)# neighbor 3.3.3.3
Switch-2(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# remote-as 200
Switch-2(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# update-source interface Loopback 0
Switch-2(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# address-family ipv4 unicast
Switch-2(conf-router-bgp-neighbor-af)# activate
Switch-2(config-router-bgp-neighbor-af)# exit
Switch-2(config-router-bgp-neighbor)# exit
Switch-2(conf-router-bgp)# neighbor 4.4.4.4
Switch-2(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# remote-as 200
Switch-2(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# update-source interface Loopback 0
Switch-2(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# address-family ipv4 unicast
Switch-2(conf-router-bgp-neighbor-af)# activate
Switch-2(config-router-bgp-neighbor-af)# exit
Switch-2(config-router-bgp-neighbor)# exit
Switch-3
Switch-3(config)# router bgp 200
Switch-3(conf-router-bgp)# router-id 3.3.3.3
Switch-3(conf-router-bgp)# neighbor 1.1.1.1
Switch-3(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# remote-as 200
Switch-3(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# update-source interface Loopback 0
Switch-3(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# address-family ipv4 unicast
Switch-3(conf-router-bgp-neighbor-af)# activate
Switch-3(config-router-bgp-neighbor-af)# exit
Switch-3(config-router-bgp-neighbor)# exit
Switch-3(conf-router-bgp)# neighbor 2.2.2.2
Switch-3(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# remote-as 200
Switch-3(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# update-source interface Loopback 0
Switch-3(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# address-family ipv4 unicast
Switch-3(conf-router-bgp-neighbor-af)# activate
Switch-3(config-router-bgp-neighbor-af)# exit
Switch-3(config-router-bgp-neighbor)# exit
Switch-3(conf-router-bgp)# neighbor 4.4.4.4
Switch-3(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# remote-as 200
Switch-3(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# update-source interface Loopback 0
Switch-3(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# address-family ipv4 unicast
Switch-3(conf-router-bgp-neighbor-af)# activate
Switch-3(config-router-bgp-neighbor-af)# exit
Switch-3(config-router-bgp-neighbor)# exit
Switch-4
Switch-4(config)# router bgp 200
Switch-4(conf-router-bgp)# router-id 4.4.4.4
Switch-4(conf-router-bgp)# neighbor 1.1.1.1
Switch-4(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# remote-as 200
Switch-4(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# update-source interface Loopback 0
Switch-4(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# address-family ipv4 unicast
Switch-4(conf-router-bgp-neighbor-af)# activate
Switch-4(config-router-bgp-neighbor-af)# exit
Switch-4(config-router-bgp-neighbor)# exit
Switch-4(conf-router-bgp)# neighbor 2.2.2.2
Switch-4(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# remote-as 200
Switch-4(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# update-source interface Loopback 0
Switch-4(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# address-family ipv4 unicast
Switch-4(conf-router-bgp-neighbor-af)# activate
Switch-4(config-router-bgp-neighbor-af)# exit
Switch-4(config-router-bgp-neighbor)# exit
Switch-4(conf-router-bgp)# neighbor 3.3.3.3
Switch-4(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# remote-as 200
Switch-4(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# update-source interface Loopback 0
Switch-4(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# address-family ipv4 unicast
Switch-4(conf-router-bgp-neighbor-af)# activate
Switch-4(config-router-bgp-neighbor-af)# exit
Switch-4(config-router-bgp-neighbor)# exit
Step 2 – Configuring eBGP between AS100 and AS200
Switch-3
Switch-1(config)# router bgp 200
Switch-1(conf-router-bgp)# neighbor 192.168.3.2
Switch-1(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# remote-as 100
Switch-1(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# address-family ipv4 unicast
Switch-1(conf-router-bgp-neighbor-af)# activate
Switch-5
Switch-4(config)# router bgp 100
Switch-4(conf-router-bgp)# router-id 5.5.5.5
Switch-4(conf-router-bgp)# neighbor 192.168.3.1
Switch-4(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# remote-as 200
Switch-4(conf-router-bgp-neighbor)# address-family ipv4 unicast
Switch-4(conf-router-bgp-neighbor-af)# activate
Verification
Verifying iBGP neighbors status
Use the command show bgp ipv4 unicast summary to check BGP neighbors status.
Switch-1
Switch-1# show bgp ipv4 unicast summary
BGP router identifier 1.1.1.1, local AS number 200 VRF default
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
2.2.2.2 4 200 39 46 0 0 00:19:58 4
3.3.3.3 4 200 6 56 0 0 00:02:05 2
4.4.4.4 4 200 7 56 0 0 00:00:35 4
Total number of neighbors 3
Total number of neighbors established 3
On Switch-1 we see 3 neighbors 2.2.2.2, 3.3.3.3 and 4.4.4.4.
Under the column Up/Down we can see the state of the neighbor. All three are UP and the time indicate the duration since the sessions were established.
Verifying iBGP neighbors details
Use the command show bgp all neighbors to see further details.
Switch-3
Switch-3# show bgp all neighbors
BGP neighbor is 1.1.1.1, remote AS 200, local AS 200, internal link
BGP version 4, remote router ID 1.1.1.1 , local router ID 3.3.3.3
BGP state = Established, up for 00:05:38
Last read 00:00:38, Last write 00:00:38
Hold time is 180 seconds, keepalive interval is 60 seconds
Minimum time between advertisement runs is 0 seconds
Neighbor capabilities:
4 Byte AS: advertised and received
Extended Message: advertised and received
AddPath IPv4 Unicast Receive: advertised and received
Route refresh: advertised and received
Multiprotocol Extension IPv4 Unicast: advertised and received
Graceful restart: advertised and received
Hostname capability advertised (name: Sonic-3) received (name: Switch-1)
Graceful restart information:
Local GR Mode: HELPER_ONLY
Remote GR Mode: HELPER_ONLY
R bit: False
Timers:
Configured Restart Time(sec): 240
Received Restart Time(sec): 240
IPv4 Unicast:
F bit: False
End-of-RIB sent: True
End-of-RIB sent after update: True
End-of-RIB received: True
Timers:
Configured Stale Path Time(sec): 720
Message statistics:
InQ depth is 0
OutQ depth is 0
Sent Rcvd
Opens: 2 1
Notifications: 0 0
Updates: 2 1
Keepalive: 6 6
Route Refresh: 0 0
Capability: 0 0
Total: 10 8
For address family: IPv4 Unicast
Address-family enabled
Prefixes received 0
Connections established 1, dropped 0
Last reset 00:05:39, Last reset reason Waiting for peer OPEN
Local host: 3.3.3.3, Local port: 34817
Foreign host: 1.1.1.1, Foreign port: 179
BGP Connect Retry Timer in Seconds 30
BGP neighbor is 2.2.2.2, remote AS 200, local AS 200, internal link
BGP version 4, remote router ID 2.2.2.2 , local router ID 3.3.3.3
BGP state = Established, up for 01:42:14
Last read 00:00:14, Last write 00:00:14
Hold time is 180 seconds, keepalive interval is 60 seconds
Minimum time between advertisement runs is 0 seconds
Neighbor capabilities:
4 Byte AS: advertised and received
Extended Message: advertised and received
AddPath IPv4 Unicast Receive: advertised and received
Route refresh: advertised and received
Multiprotocol Extension IPv4 Unicast: advertised and received
Graceful restart: advertised and received
Hostname capability advertised (name: Sonic-3) received (name: Sonic-2)
Graceful restart information:
Local GR Mode: HELPER_ONLY
Remote GR Mode: HELPER_ONLY
R bit: True
Timers:
Configured Restart Time(sec): 240
Received Restart Time(sec): 240
IPv4 Unicast:
F bit: False
End-of-RIB sent: True
End-of-RIB sent after update: False
End-of-RIB received: True
Timers:
Configured Stale Path Time(sec): 720
Message statistics:
InQ depth is 0
OutQ depth is 0
Sent Rcvd
Opens: 1 1
Notifications: 0 0
Updates: 8 5
Keepalive: 103 103
Route Refresh: 0 0
Capability: 0 0
Total: 112 109
For address family: IPv4 Unicast
Address-family enabled
Prefixes received 4
Connections established 1, dropped 0
Last reset 01:43:24, Last reset reason No AFI/SAFI activated for peer
Local host: 3.3.3.3, Local port: 179
Foreign host: 2.2.2.2, Foreign port: 40177
BGP Connect Retry Timer in Seconds 30
BGP neighbor is 4.4.4.4, remote AS 200, local AS 200, internal link
BGP version 4, remote router ID 4.4.4.4 , local router ID 3.3.3.3
BGP state = Established, up for 00:03:54
Last read 00:00:54, Last write 00:00:54
Hold time is 180 seconds, keepalive interval is 60 seconds
Minimum time between advertisement runs is 0 seconds
Neighbor capabilities:
4 Byte AS: advertised and received
Extended Message: advertised and received
AddPath IPv4 Unicast Receive: advertised and received
Route refresh: advertised and received
Multiprotocol Extension IPv4 Unicast: advertised and received
Graceful restart: advertised and received
Hostname capability advertised (name: Sonic-3) received (name: Sonic-4)
Graceful restart information:
Local GR Mode: HELPER_ONLY
Remote GR Mode: HELPER_ONLY
R bit: False
Timers:
Configured Restart Time(sec): 240
Received Restart Time(sec): 240
IPv4 Unicast:
F bit: False
End-of-RIB sent: True
End-of-RIB sent after update: True
End-of-RIB received: True
Timers:
Configured Stale Path Time(sec): 720
Message statistics:
InQ depth is 0
OutQ depth is 0
Sent Rcvd
Opens: 5 1
Notifications: 0 0
Updates: 2 5
Keepalive: 4 4
Route Refresh: 0 0
Capability: 0 0
Total: 11 10
For address family: IPv4 Unicast
Address-family enabled
Prefixes received 4
Connections established 1, dropped 0
Last reset 00:05:20, Last reset reason No AFI/SAFI activated for peer
Local host: 3.3.3.3, Local port: 179
Foreign host: 4.4.4.4, Foreign port: 39911
BGP Connect Retry Timer in Seconds 30
BGP neighbor is 192.168.3.2, remote AS 100, local AS 200, external link
BGP version 4, remote router ID 5.5.5.5 , local router ID 3.3.3.3
BGP state = Established, up for 00:09:02
Last read 00:00:02, Last write 00:00:02
Hold time is 180 seconds, keepalive interval is 60 seconds
Minimum time between advertisement runs is 0 seconds
Neighbor capabilities:
4 Byte AS: advertised and received
Extended Message: advertised and received
AddPath IPv4 Unicast Receive: advertised and received
Route refresh: advertised and received
Multiprotocol Extension IPv4 Unicast: advertised and received
Graceful restart: advertised and received
Hostname capability advertised (name: Sonic-3) received (name: Sonic-5)
Graceful restart information:
Local GR Mode: HELPER_ONLY
Remote GR Mode: HELPER_ONLY
R bit: False
Timers:
Configured Restart Time(sec): 240
Received Restart Time(sec): 240
IPv4 Unicast:
F bit: False
End-of-RIB sent: True
End-of-RIB sent after update: False
End-of-RIB received: True
Timers:
Configured Stale Path Time(sec): 720
Message statistics:
InQ depth is 0
OutQ depth is 0
Sent Rcvd
Opens: 4 4
Notifications: 6 2
Updates: 10 13
Keepalive: 12 12
Route Refresh: 0 0
Capability: 0 0
Total: 32 31
For address family: IPv4 Unicast
Address-family enabled
Prefixes received 2
Connections established 3, dropped 2
Last reset 00:09:05, Last reset reason No AFI/SAFI activated for peer
Local host: 192.168.3.1, Local port: 179
Foreign host: 192.168.3.2, Foreign port: 46778
BGP Connect Retry Timer in Seconds 30
We can see that Switch-3 has 3 iBGP neighbors: Switch-1 (1.1.1.1), Switch-2 (2.2.2.2) and Switch-3 (3.3.3.3). In addition it has one eBGP neighbor Switch-5 (5.5.5.5).
Verifying BGP database (RIB)
Use the command show bgp ipv4 unicast to display the IPv4 unicast BGP routing table, showing each advertised network, its next-hop IP, and key BGP attributes such as metric, local preference, weight, and AS path.
Switch-2
Switch-2# show bgp ipv4 unicast
Switch-2#
Notice that there are no entries in the output. That’s normal because BGP doesn’t automatically advertise routes unless configured manually.
To populate the BGP table, you can either:
- Use a network statement to advertise a specific prefix, or
- Redistribute routes from the SONiC routing table into BGP.
We will use the network statement on switches 2, 4 and 5 to advertise the networks to which the PCs are connected.
Switch-2
Switch-2# configure terminal
Switch-2(config)# router bgp 200
Switch-2(config-router-bgp)# address-family ipv4 unicast
Switch-2(config-router-bgp-af)# network 192.168.1.16/30
Switch-4
Switch-4# configure terminal
Switch-4(config)# router bgp 200
Switch-4(config-router-bgp)# address-family ipv4 unicast
Switch-4(config-router-bgp-af)# network 192.168.1.8/30
Switch-5
Switch-5# configure terminal
Switch-5(config)# router bgp 100
Switch-5(config-router-bgp)# address-family ipv4 unicast
Switch-5(config-router-bgp-af)# network 192.168.3.8/30
Now we should see some routes in the BGP table.
Switch-2
Switch-2# show bgp ipv4 unicast
BGP routing table information for VRF default
Router identifier 2.2.2.2, local AS number 200
Status codes: R - removed, S - stale, s - suppressed, * - valid
h - history, d - damped, > - best, = - multipath, q - queued, r - RIB-failure, b - backup-best, : - backup-multipath
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPref Weight Path
*> 192.168.1.8/30 4.4.4.4 0 100 0 i
*> 192.168.1.16/30 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 192.168.3.8/30 192.168.3.2 0 100 0 100 iReachability test
Ping from PC3 to PC1
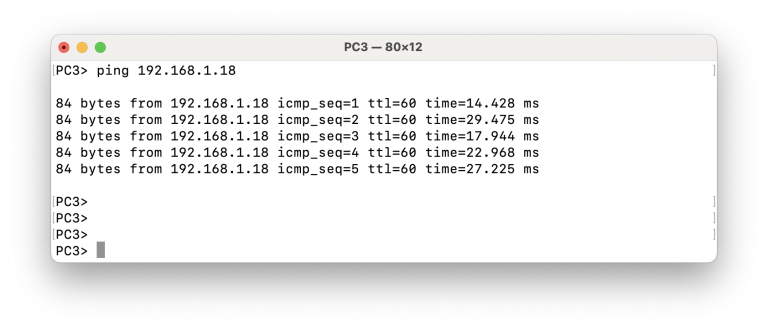
Ping from PC3 to PC2