In this article we will explore how to configure Static Routing on Enterprise SONiC. We will cover:
- Static routing overview
- Configuring a static route
- Removing a static route
- Verification
Static Routing Overview
Static routing is used to manually define routes in the routing table. Unlike dynamic routing protocols such as OSPF or BGP, static routes are fixed and do not adapt automatically to network changes. Static routes are typically used for:
- Small or simple networks
- Default routes toward upstream devices
- Backup routes in case dynamic routing fails
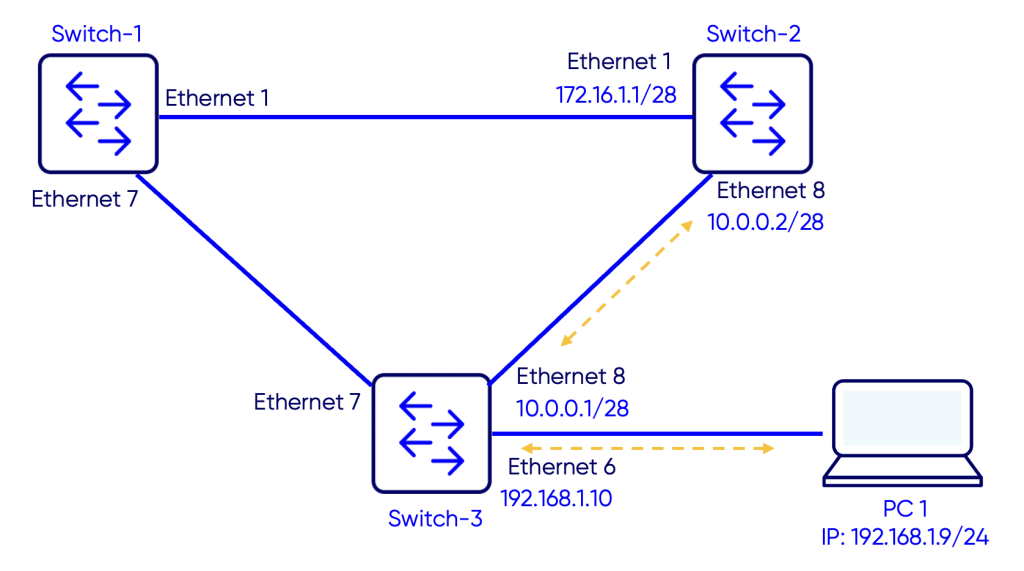
Topology
Objective
The objective is to create IP reachability between PC 1 and switch-2, more specifically IP 172.16.1.1 configured on interface Ethernet1.
Prerequisite
IP addresses are configured on the interfaces of Switch-3 and Switch-2.
Switch 2
Sonic-2# configure terminal
Sonic-2(config)# interface Ethernet6
Sonic-2(config-if-Ethernet6)# ip address 10.0.0.2/28
Sonic-2(config-if-Ethernet6)# exit
Sonic-2(config)# interface Ethernet2
Sonic-2(config-if-Ethernet2)# ip address 172.16.1.1/28
Switch 3
Switch-3# configure terminal
Switch-3(config)# interface Ethernet 6
Switch-3(config-if-Ethernet6)# ip address 10.0.0.1/28
Switch-3(config-if-Ethernet6)# exit
Switch-3(config)# interface vlan10
Switch-3(config-if-Vlan10)# ip address 192.168.1.10/28
Configuring Static Routes
Now we will configure a static route on Switch-2 to reach the PC IP address 192.168.1.9. And we will also configure a static route on Switch-2 to reach IP address 172.16.1.1/28 on Switch-2.
Switch 2
Switch-2# configure terminal
Switch-2(config)# ip route 192.168.1.0/28 10.0.0.1
Switch 3
Switch-3# configure terminal
Switch-3(config)# ip route 172.16.1.0/24 10.0.0.2
Verification
Use the command show ip route to verify the routing table:
Switch-2
Switch-2# show ip route
Codes: K - kernel route, C - connected, S - static, B - BGP, O - OSPF, A - attached-host
> - selected route, * - FIB route, q - queued route, r - rejected route, b - backup
Destination Gateway Dist/Metric Last Update
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
C>* 10.0.0.0/28 Direct Ethernet6 0/0 00:59:00 ago
C>* 172.16.1.0/28 Direct Ethernet2 0/0 00:59:00 ago
S>* 192.168.1.0/28 via 10.0.0.1 Ethernet6 1/0 00:04:14 ago
Switch-3
Switch-3# show ip route
Codes: K - kernel route, C - connected, S - static, B - BGP, O - OSPF, A - attached-host
> - selected route, * - FIB route, q - queued route, r - rejected route, b - backup
Destination Gateway Dist/Metric Last Update
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
C>* 10.0.0.0/28 Direct Ethernet6 0/0 01:00:39 ago
S>* 172.16.1.0/28 via 10.0.0.2 Ethernet6 1/0 00:00:06 ago
C>* 192.168.1.0/28 Direct Vlan10 0/0 01:00:39 ago
Testing reachability from the PC to Switch-2
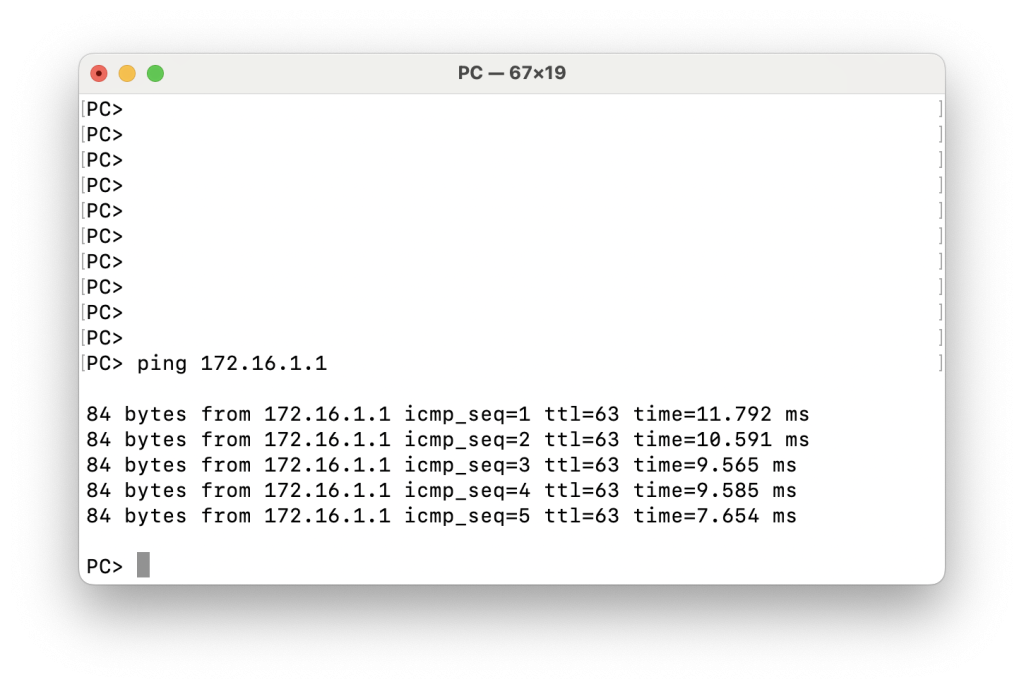
In this article, we demonstrated how to configure and verify static routing on Enterprise SONiC to establish end-to-end IP reachability. Static routes provide a simple and deterministic way to forward traffic in small or controlled environments, and they are commonly used for default routing, inter-device connectivity, or as a fallback mechanism. While static routing does not offer the adaptability of dynamic routing protocols, it remains an essential tool for network engineers and a foundational concept when building or troubleshooting SONiC-based networks.
